

Use the confidence interval to assess the estimate of the population parameter. A 95 confidence interval indicates that 19 out of 20 samples (95) from the same population will produce confidence intervals that contain the population parameter. In many cases, some of these data will be "non-detects" and, often, all these data will be "non-detects." While Process Capability can obviously be calculated from cleaning data that is above the DL, readers may assume that Process Capability is not applicable to data where some or most of the data are below the DL, since calculating a mean and standard deviation would seem impossible to do. The red confidence interval that is completely below the horizontal line does not. This situation is common with many of the analytical methods such as high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) data where the method is analyzing for only a single component and may or may not detect that component.
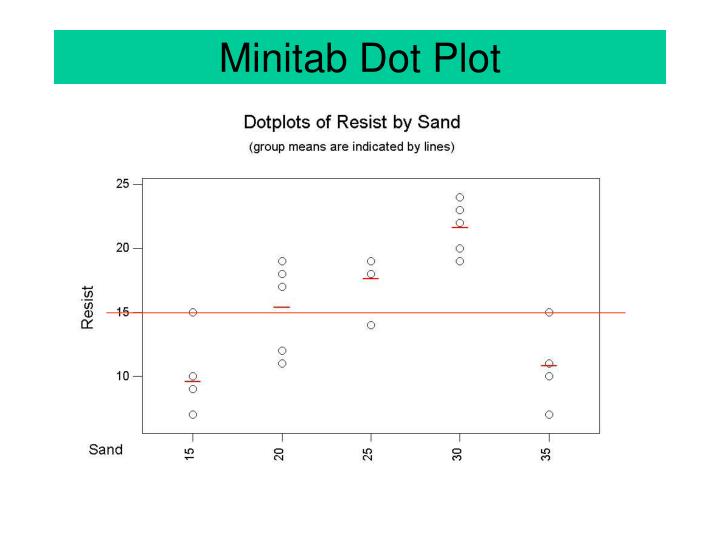
These data are known as "non-detects" or "left-censored" data.
CONFIDENCE INTERVAL MINITAB 17 HOW TO
For a more detailed explanation of where this formula comes from and additional examples on how to calculate the MTTF confidence interval for Weibull and Lognormal data, click on the second link. distributions, statistical test and confidence intervals for one and two. To see the formula used to construct the Confidence Interval for MTTF, click the first link below. A complication to the calculation of Process Capability arises when cleaning sample results are below the detection limits (DL) of an analytical method. Engineering Stats and Student Version of Mini Tab Set Douglas C. Intervals and HT on Means and Proportions page 1 of 3 Output from Minitab 17 for Confidence Intervals and Hypothesis Tests for.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
